[ad_1]
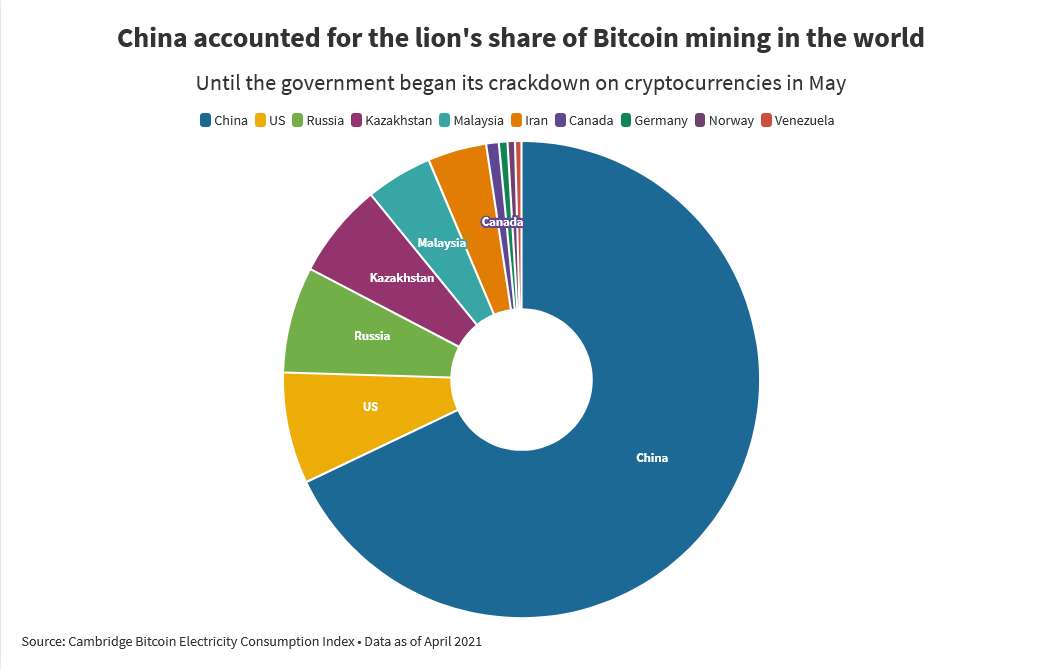
- China contributed 65% to Bitcoin’s hash rate, but that’s expected to see a sizable drop after the Asian giant’s crackdown on mining.
- Bitcoin was inherently designed to tackle a drop or rise in its hash rate. It does this by implementing a concept called ‘the
mining difficulty ’. - The short-term fall in hash rate shall soon be bridged as new farms slowly come back online after China’s mining community sets up shop in other countries.
Bitcoin’s net worth has
corrected radically, and its hash rate is at a six-month low, despite broader adoption and acceptance from lawmakers across the globe. China decided to
crack down on miners in May, and the ripple effects of the country-wide decision are finally being felt globally.
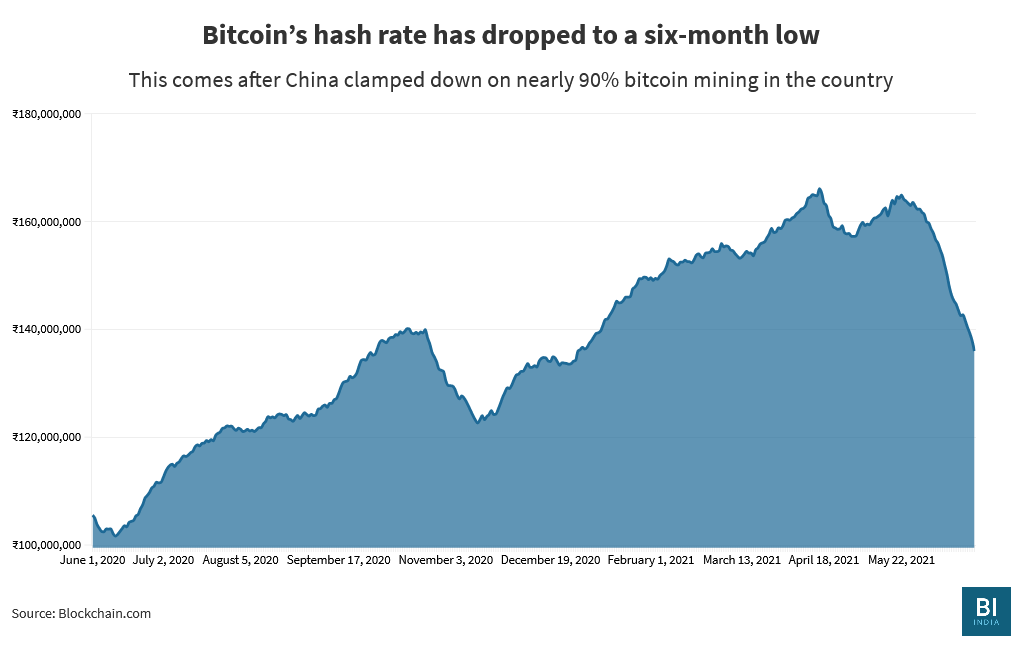
Bitcoin’s hash rate was on an uptrend in 2021, hitting 168,000 petahashes per second (PH/s) on May 15. It has since dropped by 40% to nearly 86,000 PH/s as of June 23. Most Chinese Bitcoin
pools like AntPool and F2Pool have witnessed a drop of more than 50% in their hash rate.
Simply put, a drop in the hash rate means chances of landing on the correct hash to earn Bitcoin are very low. In addition to miners from China trying to shift shop offshore as soon as possible, Bitcoin has an inbuilt safeguard that will push hash rates level back up with time.
What is Bitcoin’s hash rate?
In simple words, hash rate means the total computational power required to mine a Bitcoin. Where central banks issue fiat currencies, new Bitcoins are issued to miners via a block reward for solving a block.
China contributed 65% to Bitcoin’s hash rate, but a great exodus is underway as miners are packing bags from the fertile lands of Sichuan, looking for greener pastures in the West.
Advertisement
Bitcoin leverages the SHA-256 Cryptographic Hash Algorithm, which requires a certain number of zeroes to unlock the block. Today, Bitcoin miners have to find a hash that starts with nineteen zeroes. Hence, miners use top-notch chips or GPUs to make the mathematical process as fast as possible.
Simply put, it’s like trying to open a lock with every possible combination. In the case of Bitcoin, the miner tries to find the hash value to close the block and add it to the networked blockchain.
With each block getting solved, the miners are rewarded with Bitcoins and other transaction fees. This artificial mining process helps control the supply of coins and the fastest finger first, wins.
The hash rate rises as more miners and equipment are added to the network. And, it falls when miners disappear from the system.
Fear not, Bitcoin has an inbuilt safeguard
Bitcoin was inherently designed to tackle a drop or rise in its hash rate. It does so by implementing a concept called ‘the mining difficulty’, which determines how difficult it should be for miners to complete finding a hash.
This was done to ensure that a new block gets added to the
blockchain remotely or at a stable pace every 10 minutes. Due to the sudden fall in hash rate, the average block production time rose to 12 minutes.
However, the blockchain self-adjusts. It has the mechanism to make it easier for miners by reducing the difficulty level. By doing so, it will become simpler for everyone in the network to find new hashes, while those who’re left offline shall miss out on the temporary easing.
Chinese crypto industry will be fine even if all of its mining was offshore
The reduction in the difficulty level of mining for Bitcoin is the prime reason why miners in China are
scrambling to shift camp and move to the West, where green energy is easier to access, and lawmakers are welcoming.
“As more hash rate falls off the network, the difficulty will adjust downwards, and the hash rate that remains active on the network will receive more for their proportional share of the mining rewards,” Kevin Zhang, vice president of crypto mining firm Foundry, told
CNBC.
Many experts aren’t too concerned since a massive migration effort is already underway, often dubbed ‘
the great mining migration.’ It means that miners aren’t going to stop mining because China said so. They are actively moving out of China and opening new farms in the US, Kazakhstan, Russia, and more.
Transactions can be assembled and included in blocks anywhere. The Chinese crypto industry would work perfectly well even if all mining was domiciled offshore.The short-term fall in hash rate shall soon be bridged as new farms slowly come back online.
Many mining farms based out of the US, like Foundry USA, witnessed no fall in their hash rate and actually posted positive growth while Chinese counterparts were shutting down.
With the large-scale exodus ongoing from China and multiple countries showing interest in
adopting Bitcoin as legal tender, it’s safe to assume the current crash is temporary.
For a more in-depth discussion, come on over to Business Insider Cryptosphere
— a forum where users can deep dive into all things crypto, engage in interesting discussions and stay ahead of the curve.
SEE ALSO:
World’s largest Bitcoin mining rig seller isn’t taking any new orders for foreseeable future
China’s Bitcoin miners are looking at US, Kazakhstan, Canada, and Europe amid the exodus — but not every option fits the bill
[ad_2]


